 00389 2 3091 484
00389 2 3091 484
Medical services
Cardiology
Cardiologic investigations
Cardiovascular assessment
- ECG
- Heart ultrasound examination
- Doppler of neck blood vessels
- Doppler of peripheral blood vessels
- Examination of aorta
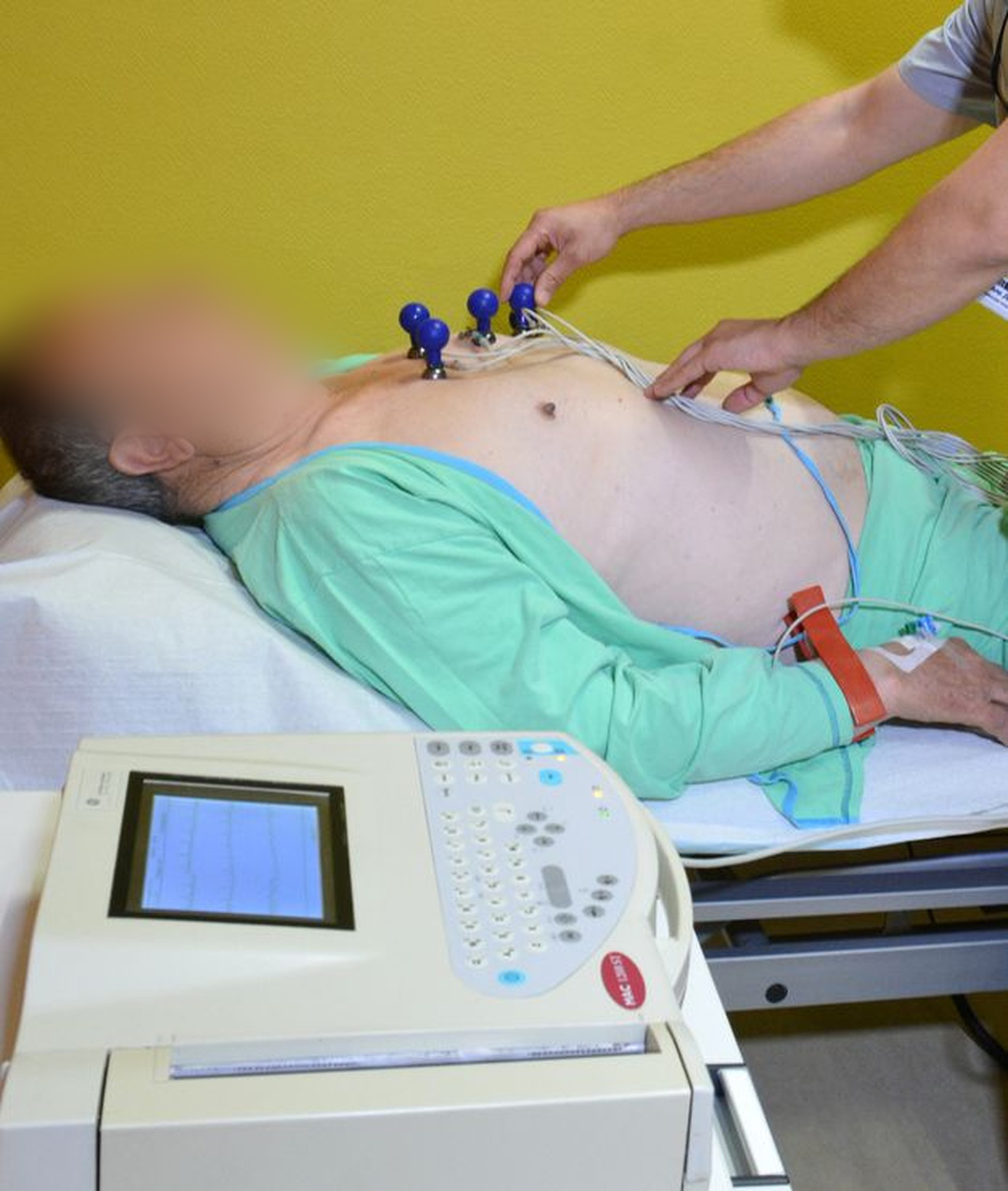
Electrocardiogram – ECG
An electrocardiogram is a diagnostic test of the electrical function of the heart. Each change in the look of the waves shown in the ECG recording indicates the same irregularity in certain heart function.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Holter monitor
ECG Holter monitor investigates the electric function of the heart for a 24-hour period, sometimes even for 48-hour period. This diagnostic procedure monitors the heart rhythm for a longer period since some conditions which disrupt the heart rhythm occur sometimes or during sleep, change of the body position, psychical stress and physical activity.
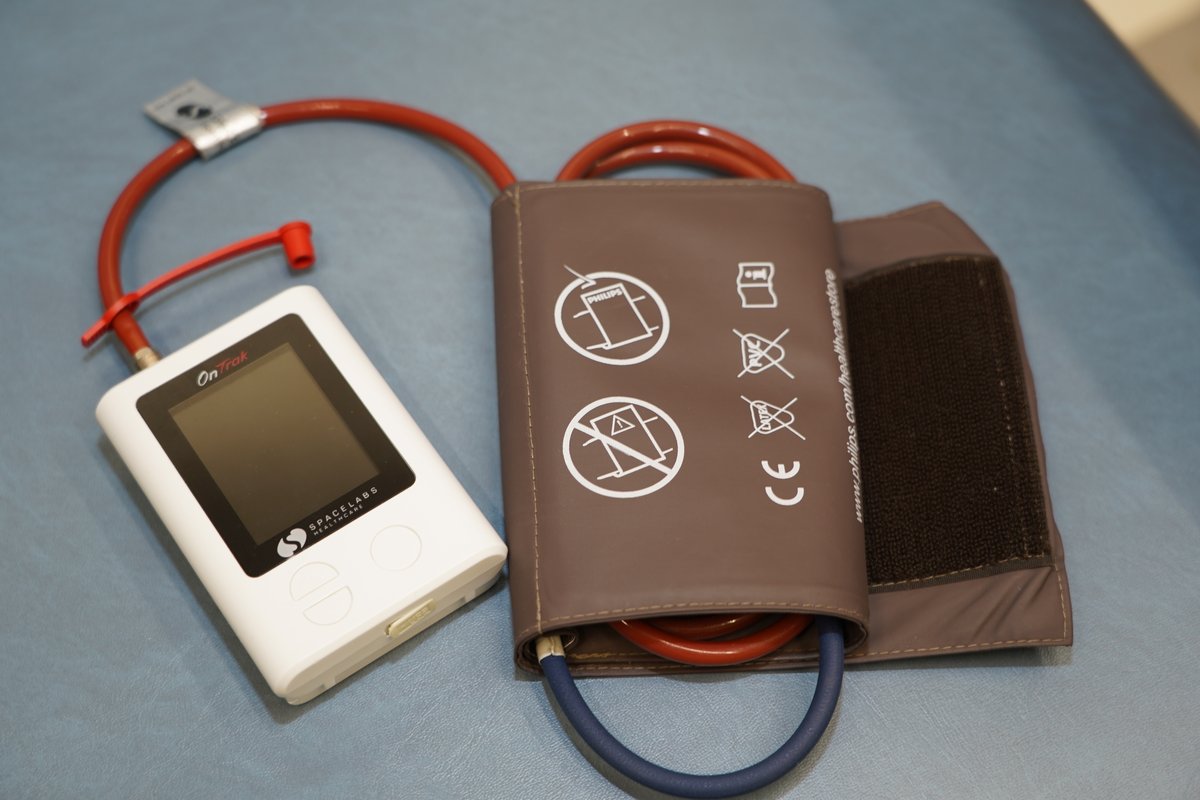
Blood pressure monitoring (ABP) Holter monitor
Blood pressure monitoring (ABP) Holter monitor is used to measure the blood pressure in a period of 24/48 hours during day-to-day activities. The objective of this diagnostic method is to monitor the variations of the blood pressure in certain period and determination of proper medication therapy or modification of the existing one.
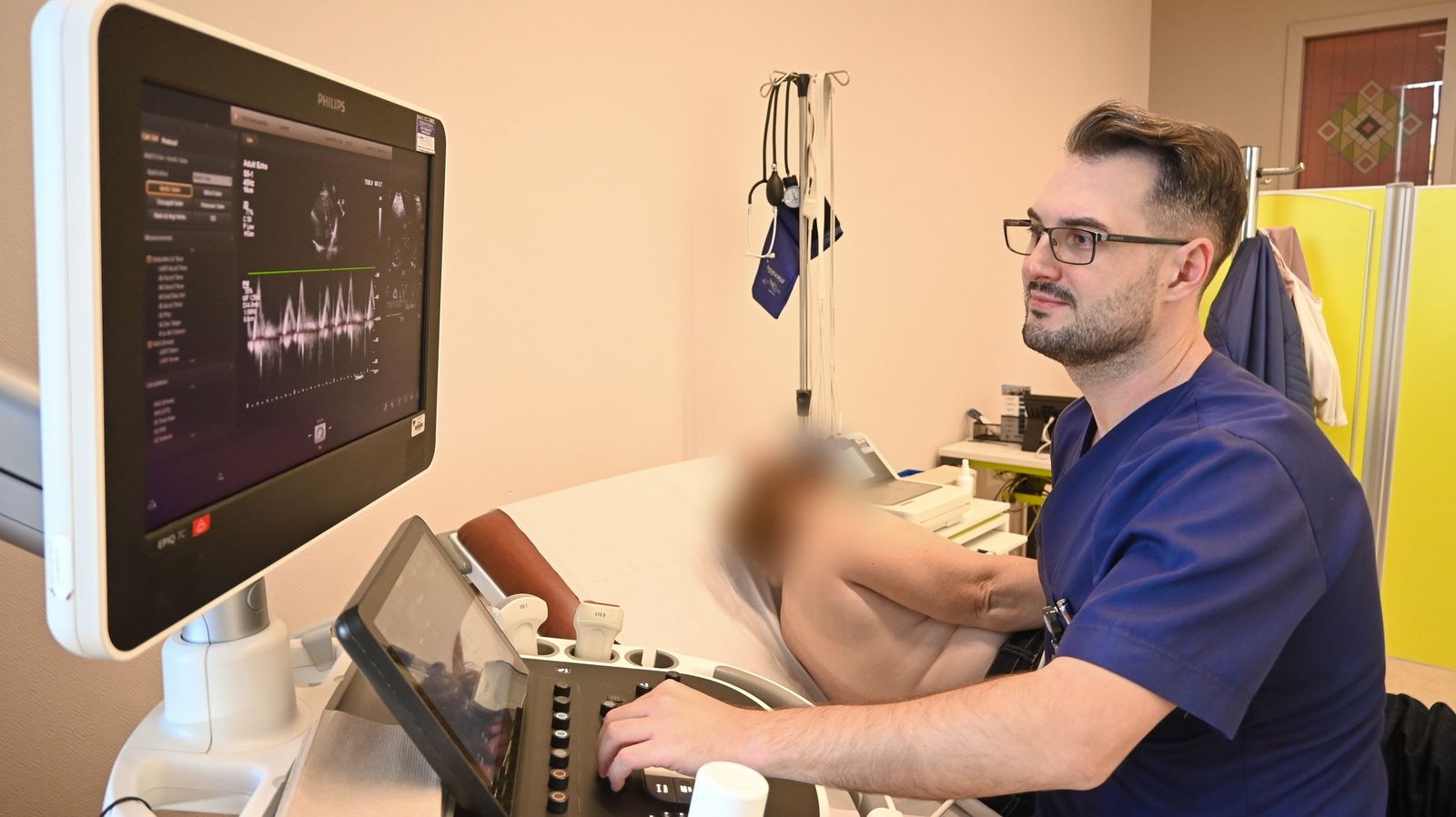
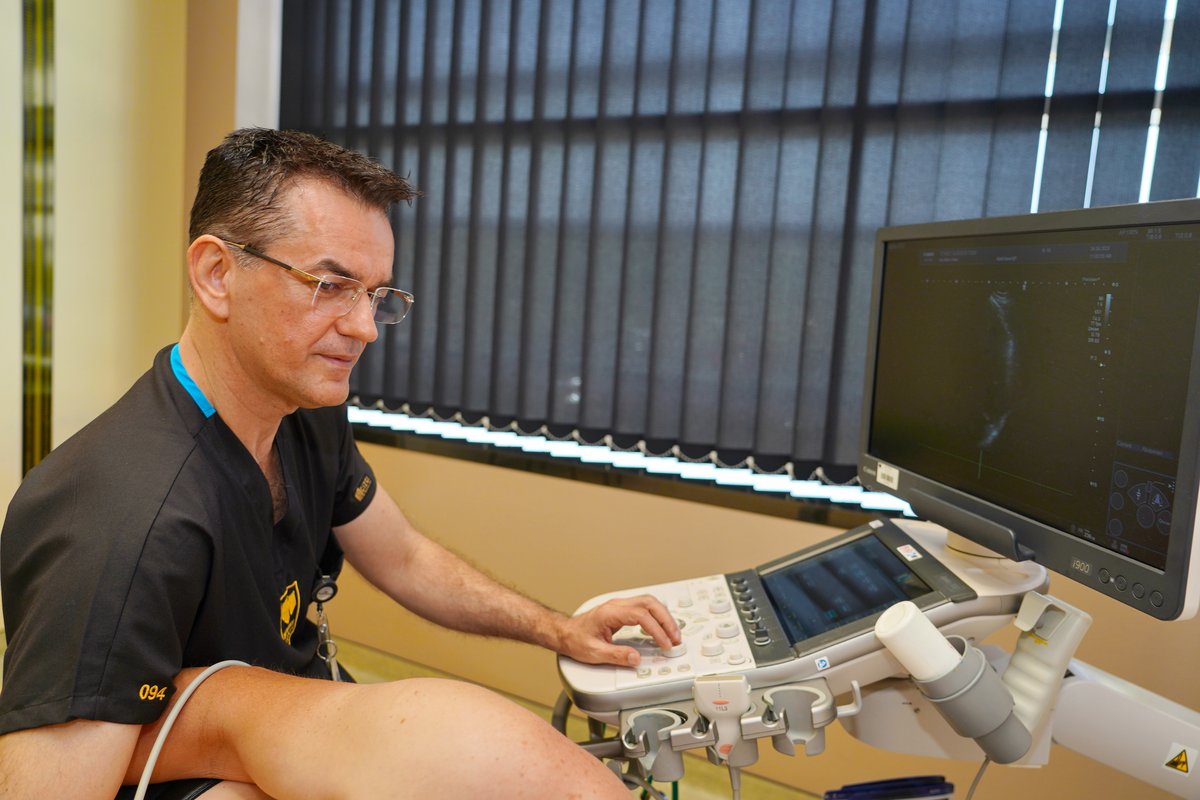
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)
Transthoracic echocardiography is a standard diagnostic non-invasive technique which provides moving image of the heart cavities using ultrasound which is directed to the chest using a probe. This technique enables assessment of the heart pump strength, the condition of the valves (heart murmur), change of the dimensions of the heart, indirect detection of infarction, pulmonary hypertension, endocarditis, pericarditis, heart failure, diastolic function and ventricular dyssynchrony.

Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is a diagnostic procedure which is performed through a special probe attached to the end of a flexible hose which is inserted into the esophagus after application of a local anesthesia.
TEE has two main advantages:
- Enables better review of the heart structures, especially the heart septum and the structure and form of the heart cusps.
- Application during cardiovascular surgery and cardiological interventions.
Indications for TEE are:
- Investigation of the cause of stroke due to existence of small channel in the atrial septum which cannot be seen with transthoracic echocardiography
- Detecting thrombi in the heart cavities in persons with arrythmia
- Diagnosis endocarditis
- Assessment of the function of the implanted artificial valves
- Assessment of the aortic wall structure.
Coronary stress test
Coronary stress test is used to assess the effect of physical stress on the heart.
Indications for implementation of such investigation include anginous symptoms, in conditionally health patients with several risks for cardiovascular diseases, assessment of the origin of the symptoms such as breathlessness and fatigue, provoking irregular rhythm, control of the effects of the antihypertension therapy.
Stress echocardiography
Stress echocardiography is an investigation which uses ultrasound techniques to determine the reaction of the heart muscle during physical, pharmacological or electrical stress. It is a painless procedure which achieves similar diagnostic and prognostic accuracy like the radionuclide perfusion tests, but at a fraction of the cost, without the negative environmental impact and without consequences for the patient and the physician.
The accuracy of stress echocardiographic investigation in order to reveal a significant coronary disease is between 80% and 90% and exceeds the classical coronary stress test, especially in women and patients with left ventricular hypertrophy (thickening). Stress echocardiography is a powerful prognostic tool in chronic coronary disease, after a myocardial infarct and in evaluation of patients before a big non-cardiac surgery. It is used to assess the kinetics of the left ventricle wall, assessment of the viability of the myocardium and assessment of the extent of an aortic stenosis.
There are several indications for stress echocardiographic investigation.
A. Diagnosis of coronary disease:
1.Patients in whom stress test is contraindicated
2.Patients in whom stress test is impossible to perform (for example, patients who have difficulty of movement, due to problems with knees, hips etc.)
3.Patients with undiagnosed or borderline coronary stress test
4.Block of the left branch. Stress test of submaximal values (for example, patients with poor physical condition)
5.Assessment of the viability in high-risk patients for coronary bypass surgery (whether the patient would benefit from a bypass surgery.
B. Prognosis and stratification of risk in patients with known coronary disease
C. Assessment of the surgical risk
D. Evaluation of the heart etiology of dyspnea (lack of air during stress)
E. Evaluation after revascularization
F. Ischemia location
G. Evaluation of the severity of a valvular stenosis.
Stress echocardiography investigation can be performed using dobutamine, dypiridamole or using a bike. Dobutamine echo is better for patients with bronchial asthma or problems with the heart conductive system, while dypiridamole test is recommended in patients with severe arrythmias or severe hypertension. Stress echocardiography using a bike is most physiological and functional investigation used to assess the heart kinetics during rest and after stress.
The investigations last 20-30 minutes in an outpatient setting.
Stress echocardiography is a standard method in the Zan Mitrev Clinical Hospital.
Transcranial Doppler
It is a non-invasive method which is usually used for assessment of a stroke risk in adults under 50 years of age caused by patent foramen ovale (PFO) or channel in the heart atriums which is usually lost after birth.
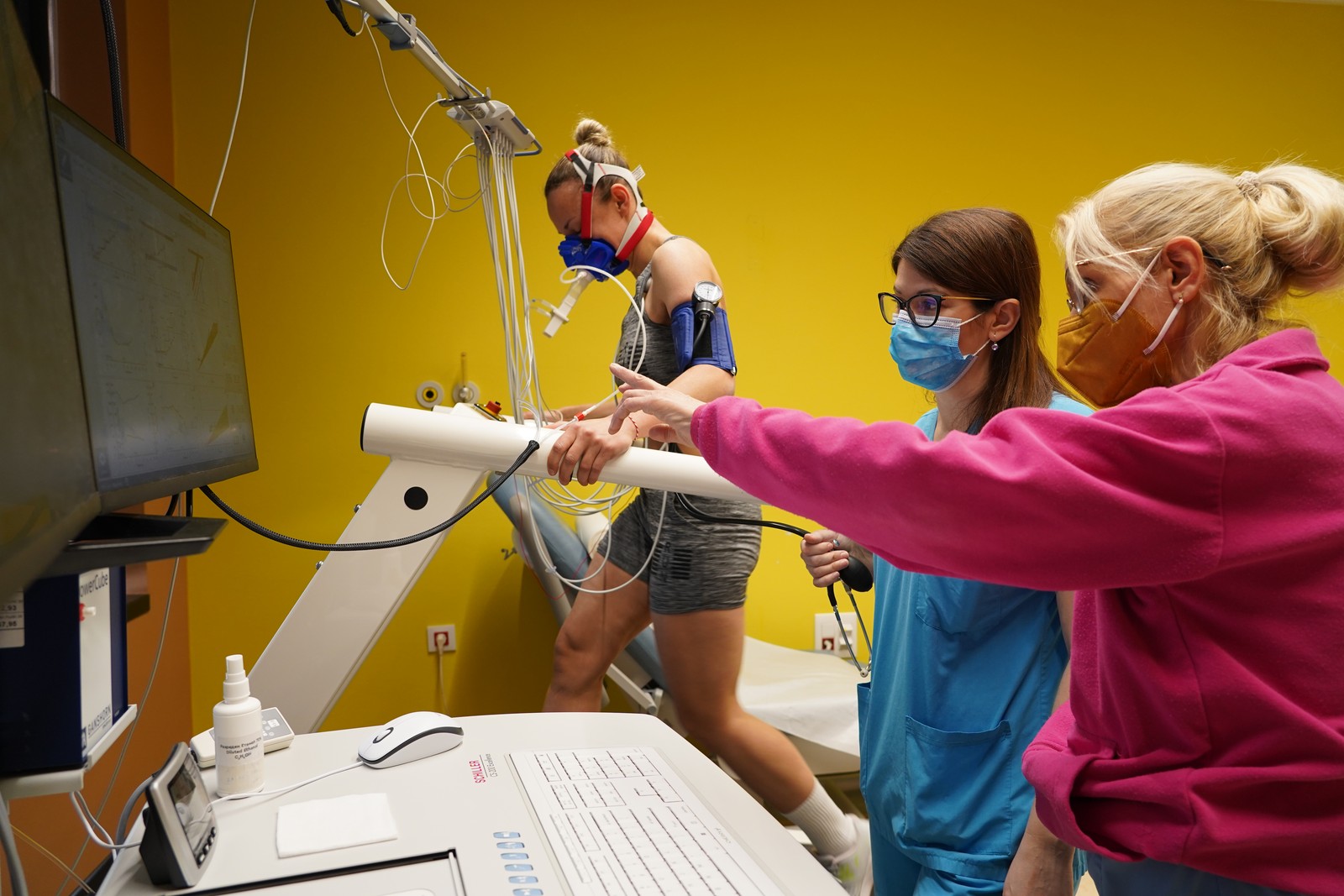
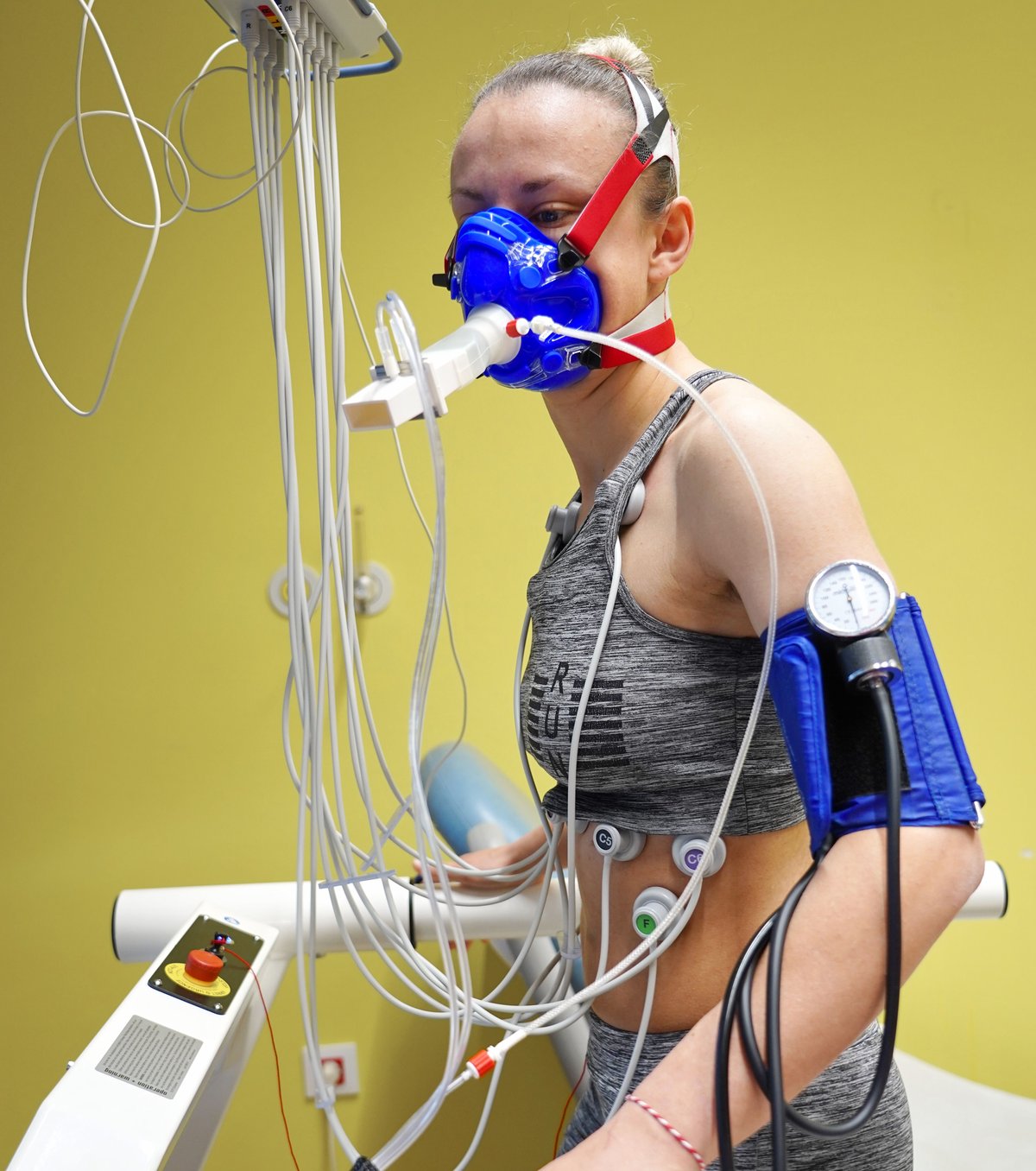
Ergospirometry
Cardiopulmonary stress test (CPET), also known as ergospirometry is a test which measures the work of the heart in correlation with the lungs during physical stress.
Unlike the standard stress test, the patient walks on a treadmill or rides a static bike with installed additional devices. They include blood pressure monitor, ECG electrodes (electrocardiogram – ECG) which record the heart activity as well as mask on the face which measures the oxygen consumption i.e. breathing frequency and intensity, how often and how deep the patient inhales and exhales.
Other doctor’s from this department

Ass. Prof. Oliver Bushljetic MD
Specialist in internal medicineSubspecialist in Cardiology
oliver.bushljetikj@zmc.mk

Vilma Ampova Sokolov MD
Specialist in internal medicine - subspecialist cardiology
vilma.ampova@zmc.mk

Snezhana Bongard MD
Specialist in internal medicine Subspecialist in cardiology
snezhana.bongard@zmc.mk

Ass. Prof. Tanja Angjusheva MD
Specialist in internal medicine
Subspecialist in cardiology
tanja.anguseva@zmc.mk

Borjanka Georgieva MD
Specialist in internal medicine
Subspecialist in cardiology
borjanka.georgieva@zmc.mk

Enver Idoski MD
Internal Medicine SpecialistSub spec. in cardiology
enver.idoski@zmc.mk

Shpend Idrizi MD
Specialist in internal medicineSubspecialist cardiology
shpend.idrizi@zmc.mk

Prof. Milka Klincheva MD, PhD
Specialist in internal medicinesubspecialist in cardiology
milka.klinceva@zmc.mk






